Read about START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
In piping systems sudden changes in flow cause pressure unbalanced forces between elbows, valves, tees, reducers, and other in-line components. These forces damage the piping system when it is not properly designed to accommodate them.
The main advantage of using PASS/START-PROF and PASS/HYDROSYSTEM is that 3D piping model can be easily converted between these software packages both ways.
3D piping model from PASS/START-PROF can be converted into 3D piping model in PASS/HYDROSYSTEM, then generate 3D water hammer loads for all nodes at certain moments of time (not only just in one node!) and pass it directly into stress analysis software PASS/START-PROF automatically.
The water hammer loads are calculated using PASS/Hydrosystem software, then exported to PASS/START-Prof to perform the pipe stress analysis. The algorithm is following:
The loads that exported to PASS/START-PROF are calculated in PASS/Hydrosystem the following way:
You can find more detailed description of this algorithm in PASS/Hydrosystem user guide.
PASS/START-PROF and PASS/HYDROSYSTEM allows us to model it very easy, just in several clicks, and help to find a way to reduce water hammer damage of the piping system. Let’s study how to perform stress analysis of the piping system from water hammer loads.
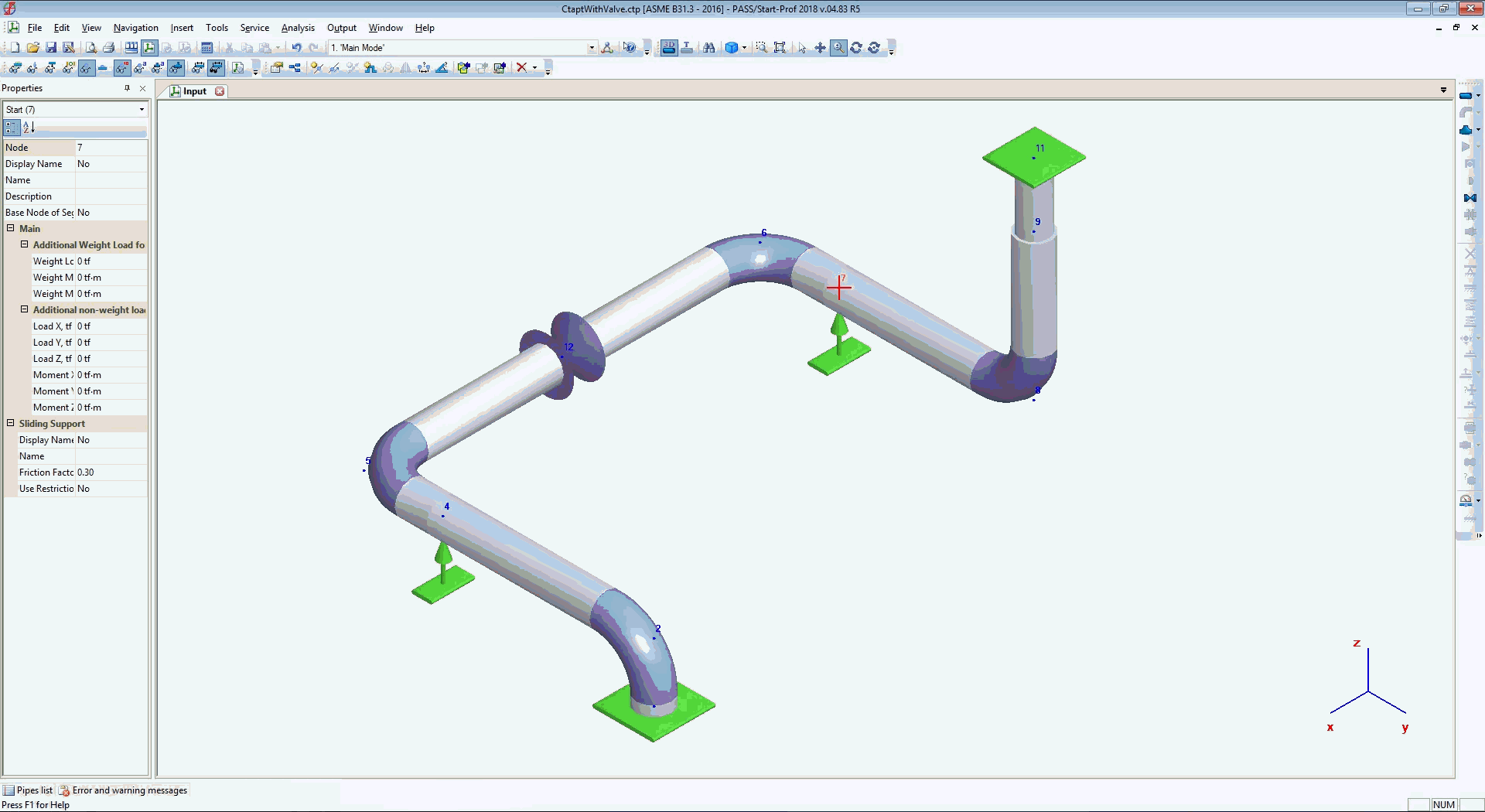
The simple piping system created in PASS/START-PROF software is shown on below screenshot:
After saving the PASS/START-PROF file, we can open it using PASS/HYDROSYSTEM software.
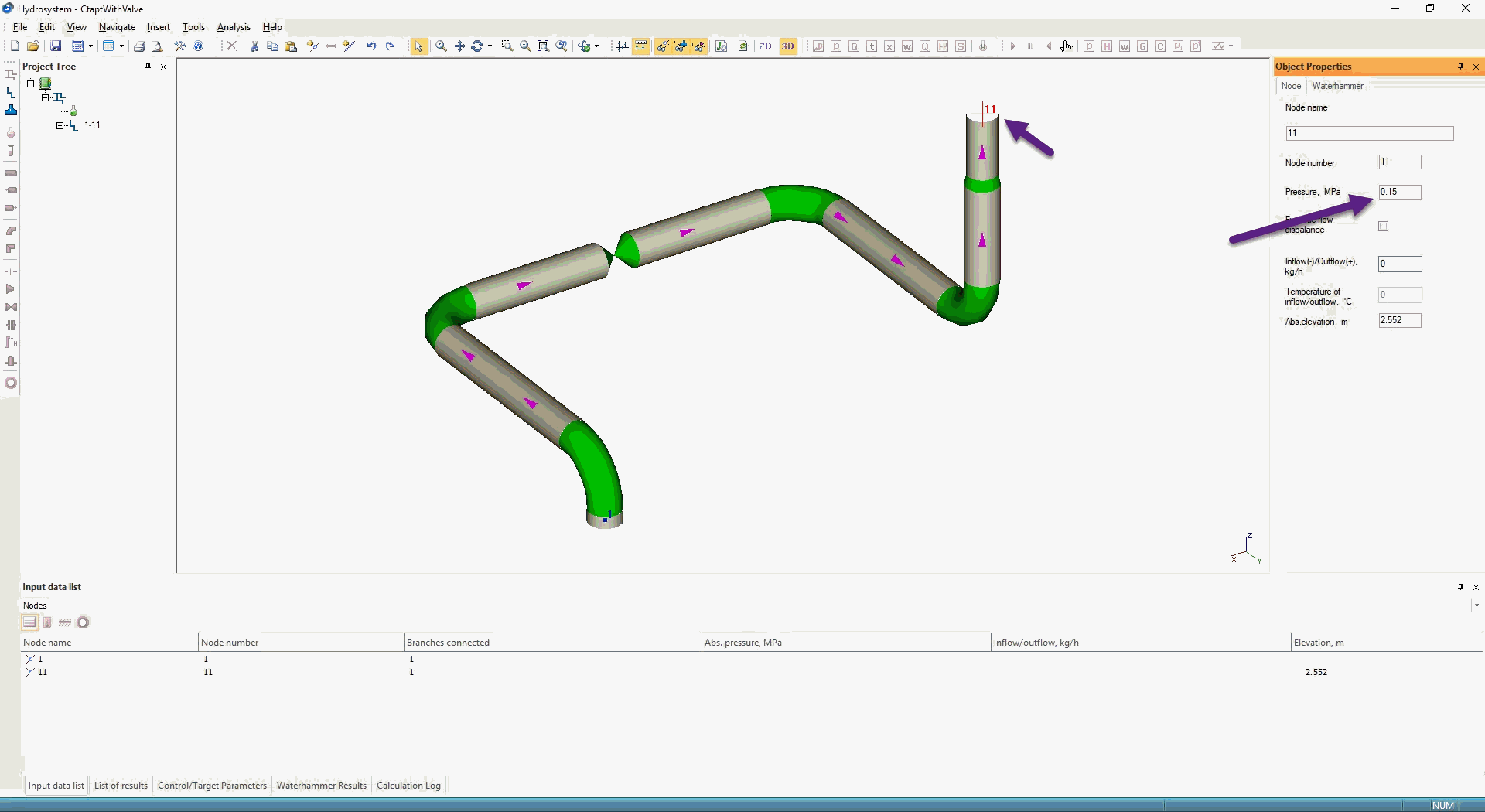
Set pressure 0.15 MPa at node 1, and 0.16 MPa at node 11
Choose water steam library
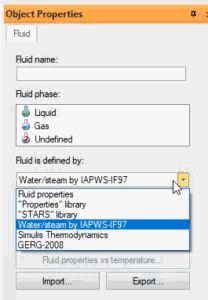
Define the period of surge analysis 2.5 sec, data output stem 0.01 sec, and dynamic load factor DLF=2.0.
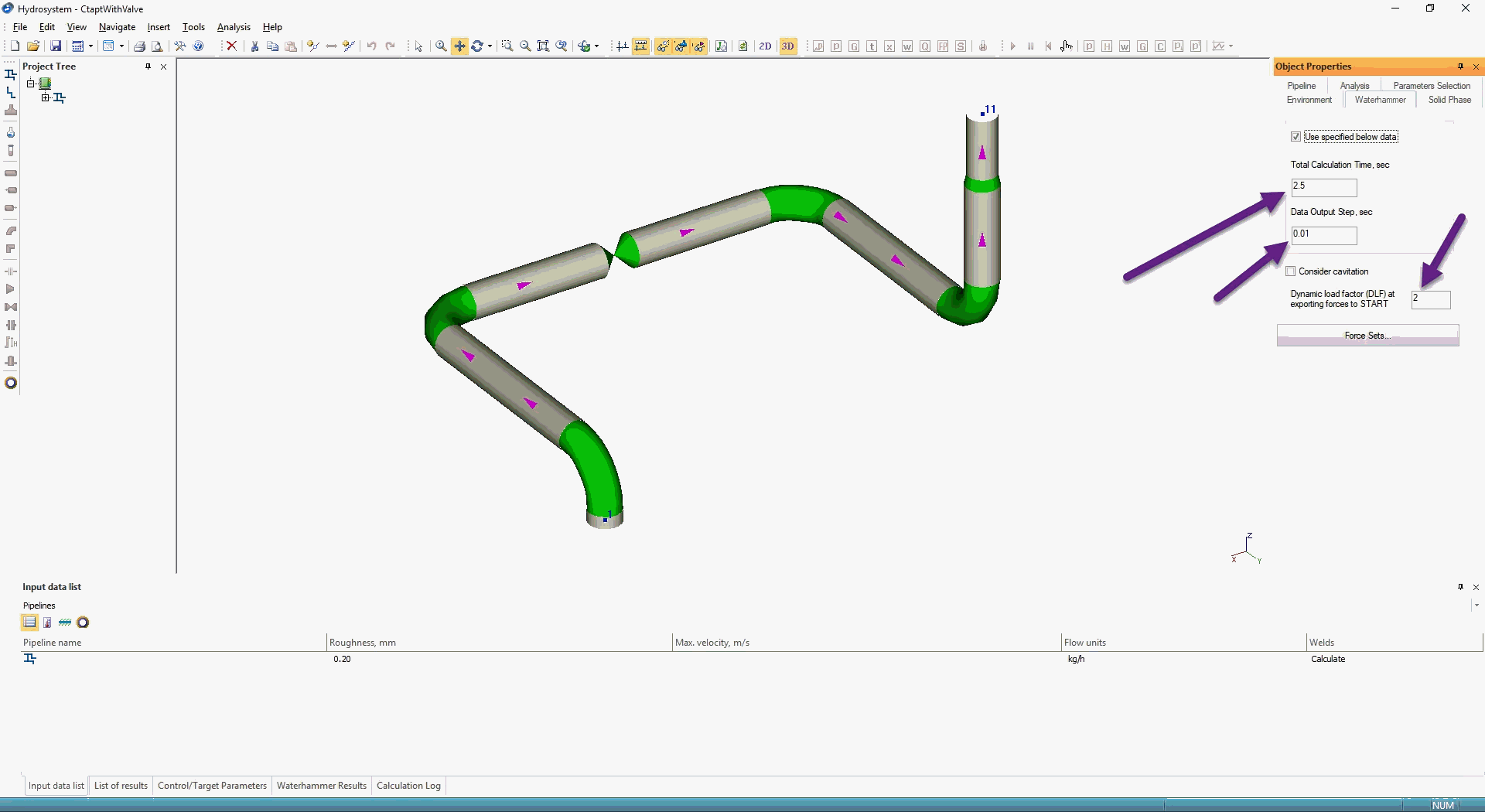
Select Valve in node 12 and in the “Waterhammer” tab set that valve is immediately closed.
Run Isothermal Flow analysis
Run water hammer analysis
After that export unbalanced pressure forces into (.ctpf) file. Also HYSROSYSTEM allows to export data into (.frc) file that can be opened by CAESAR II.
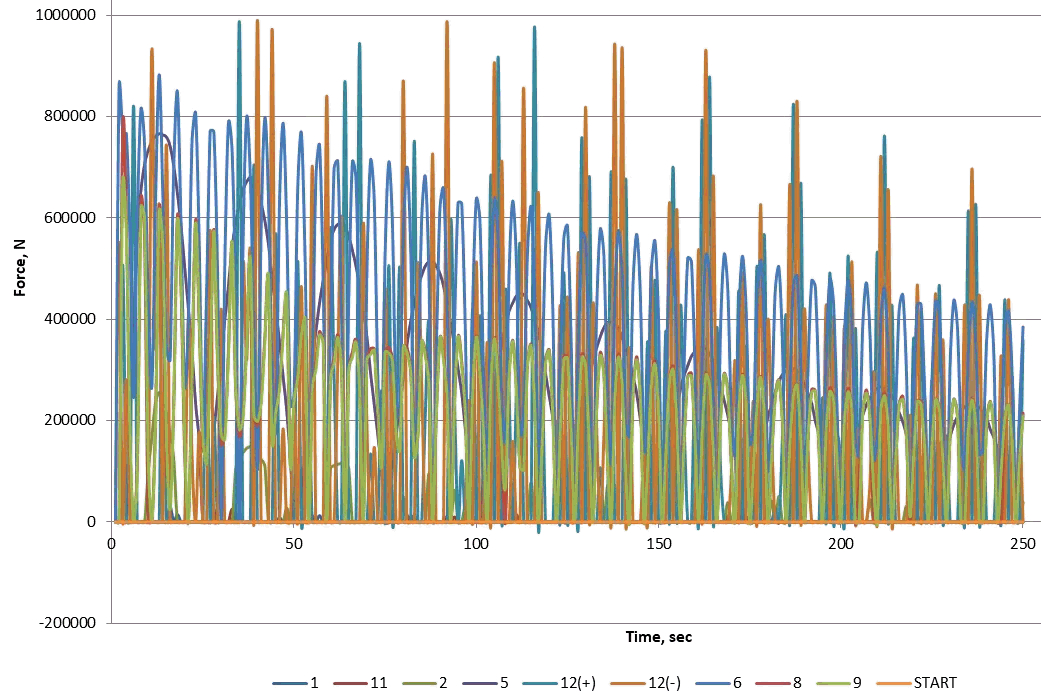
(.ctpf) file contains forces multiplied by DLF factor for all nodes in piping models at several most dangerous moments of time. The most dangerous moments of time is found automatically by HYROSYSTEM software.
This is the (.ctpf) file structure

This means, that PASS/HYDROSYSTEM generates unbalanced pressure loads for all nodes in the piping system at a certain moment of time.
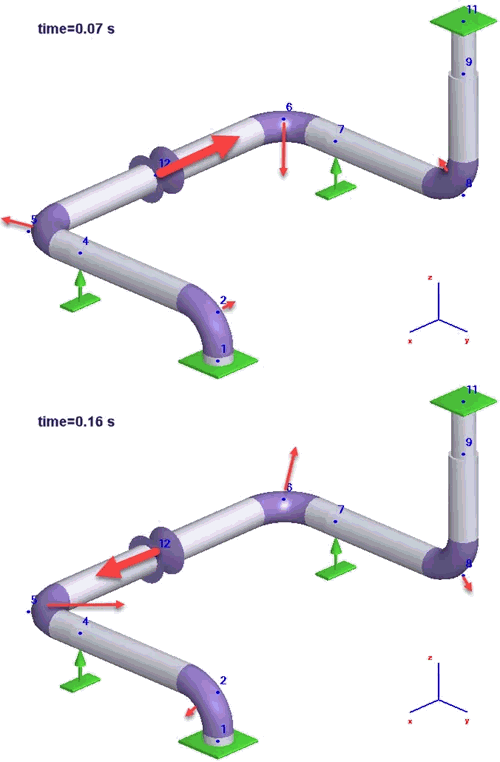
Now open PASS/START-PROF, open Operation Mode Editor and import waterhammer forces into first operating mode.
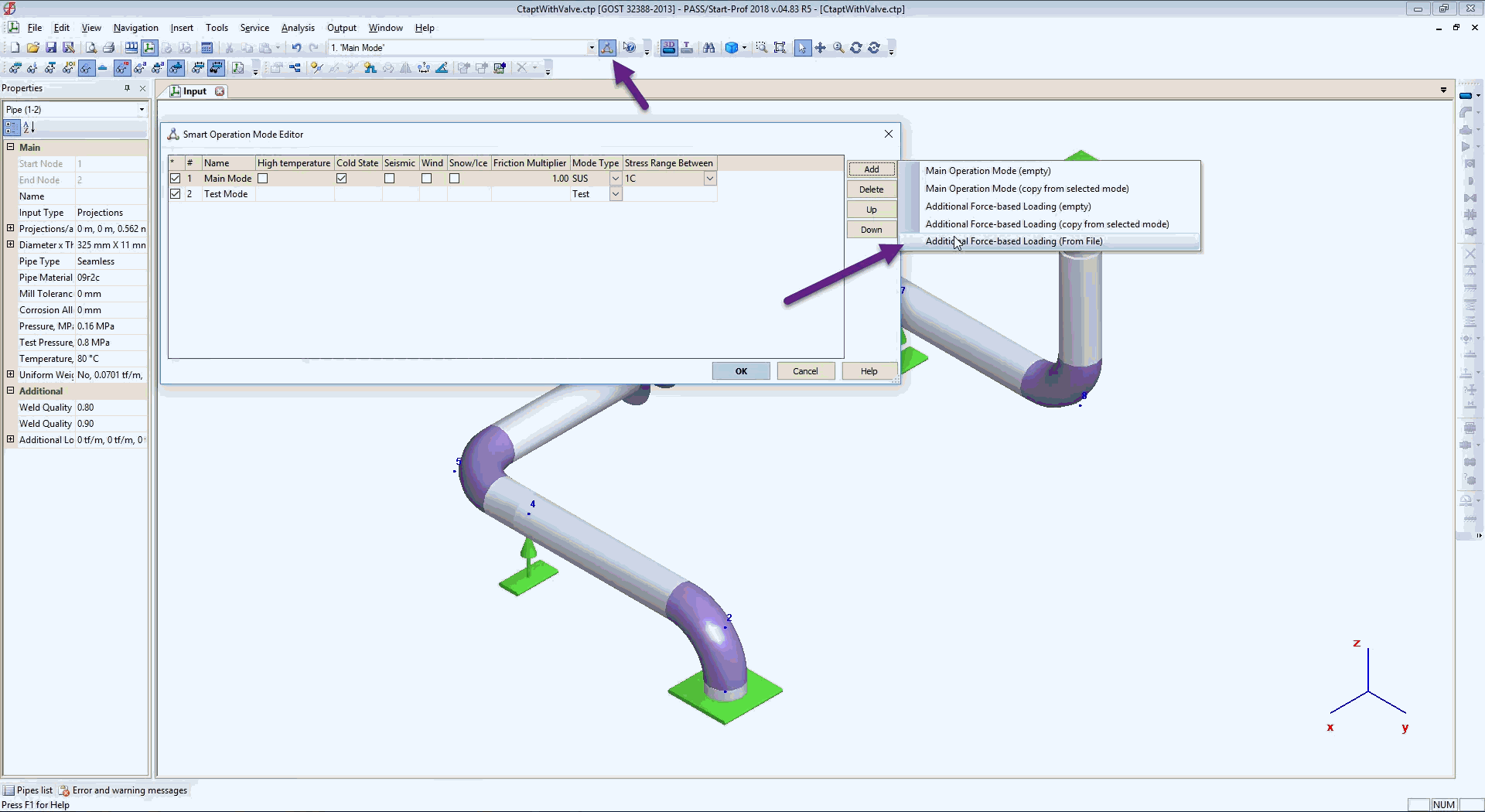
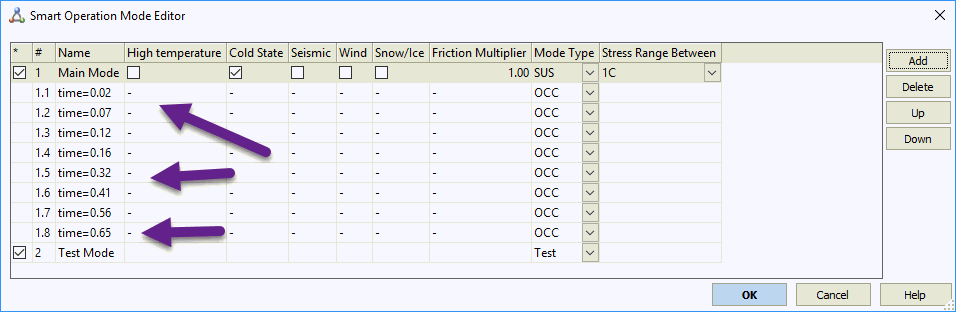
Eight additional force-based load cases are imported from the file
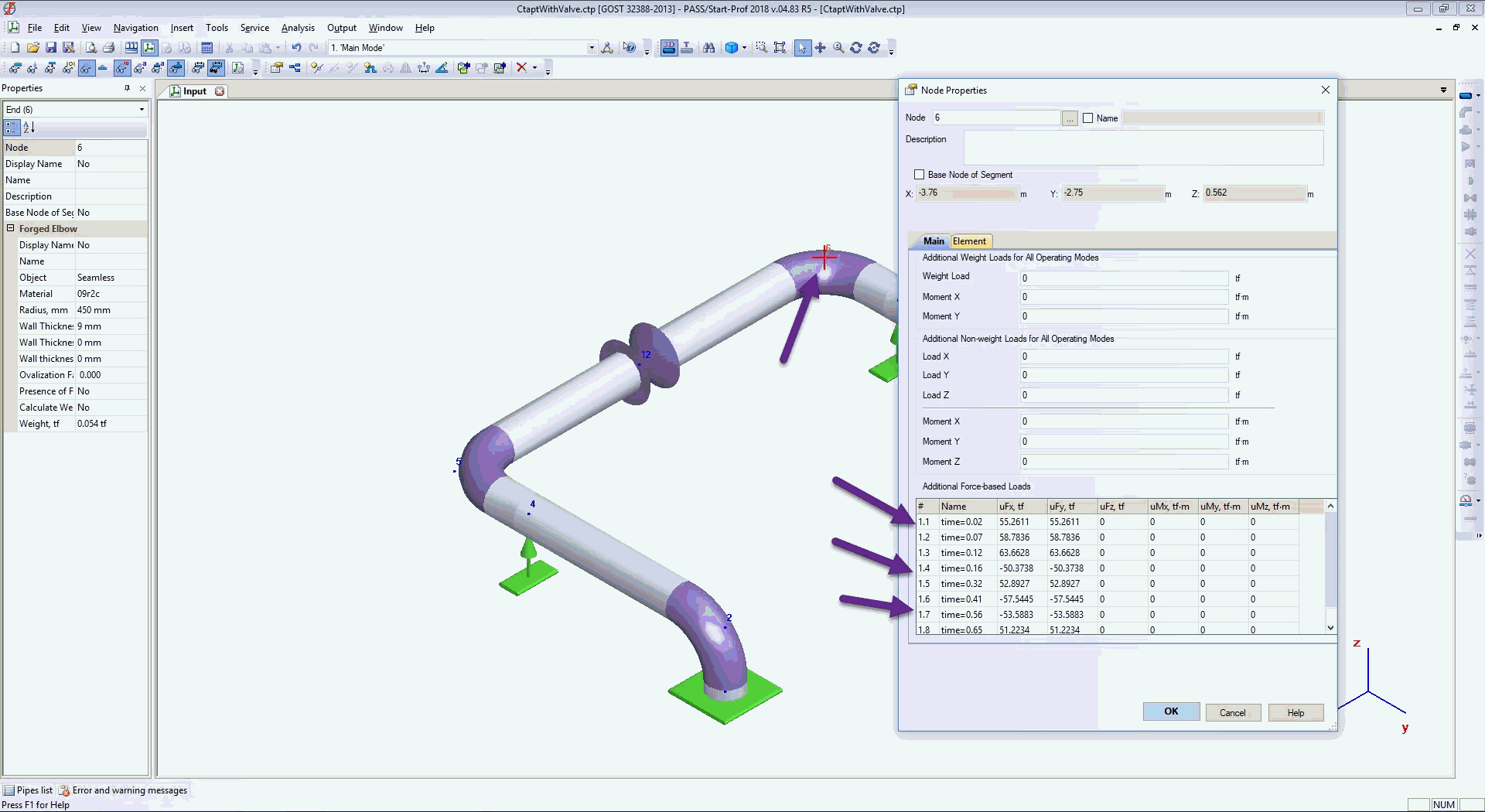
You can check the force values at any node properties
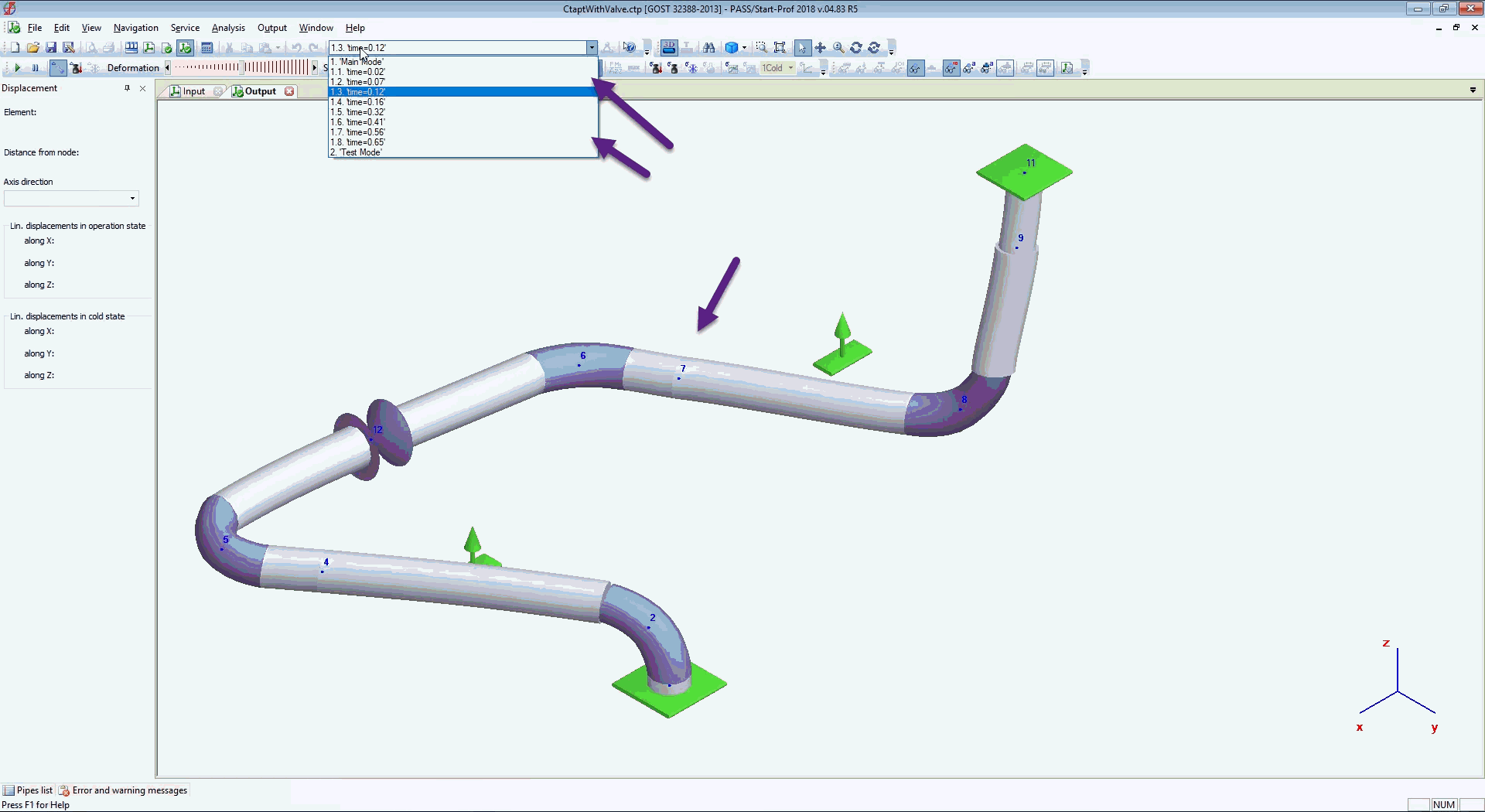
Now run piping stress analysis and see results
Deformed Shape at any moment of time
Stress table at any moment or time
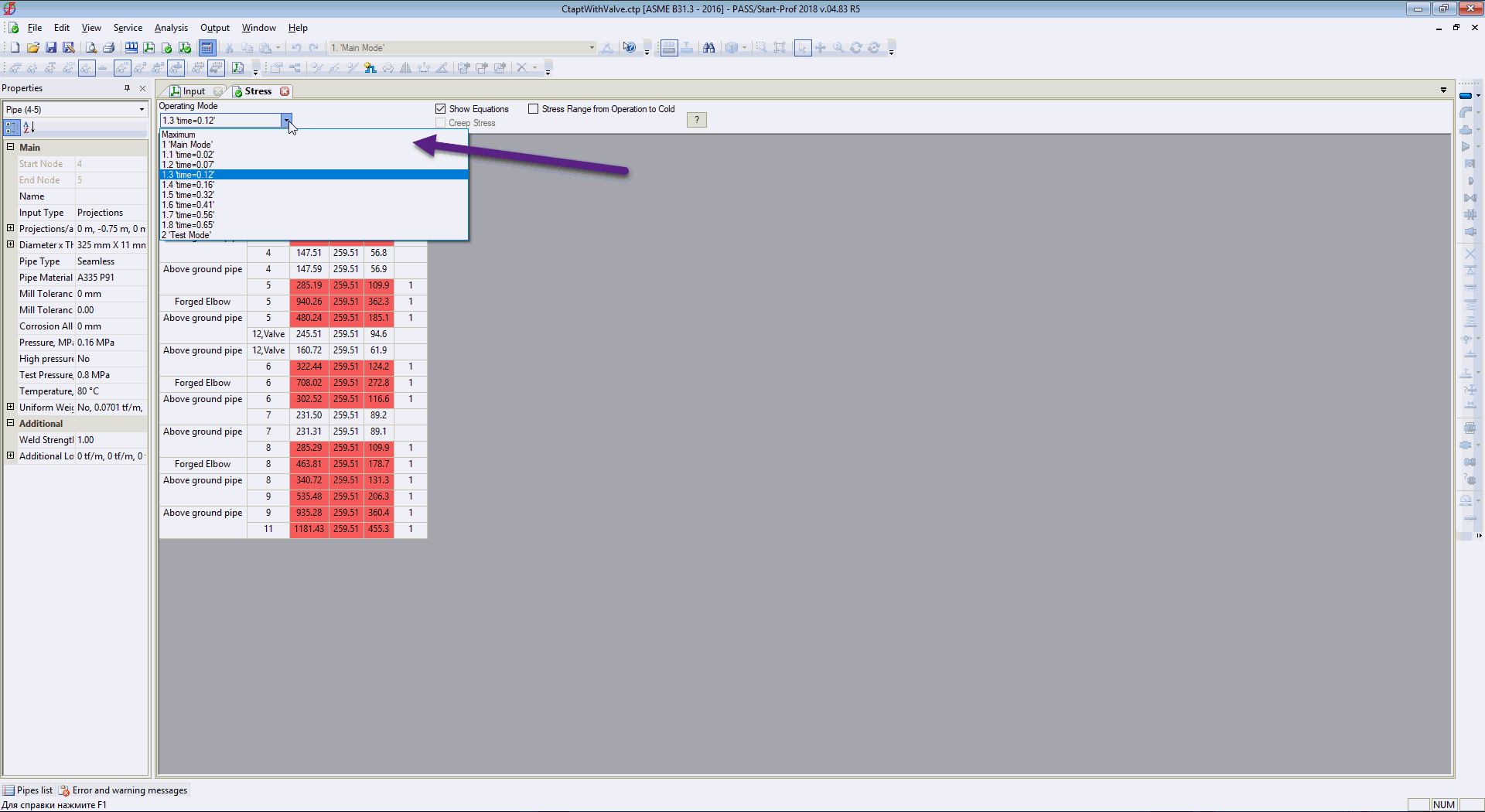
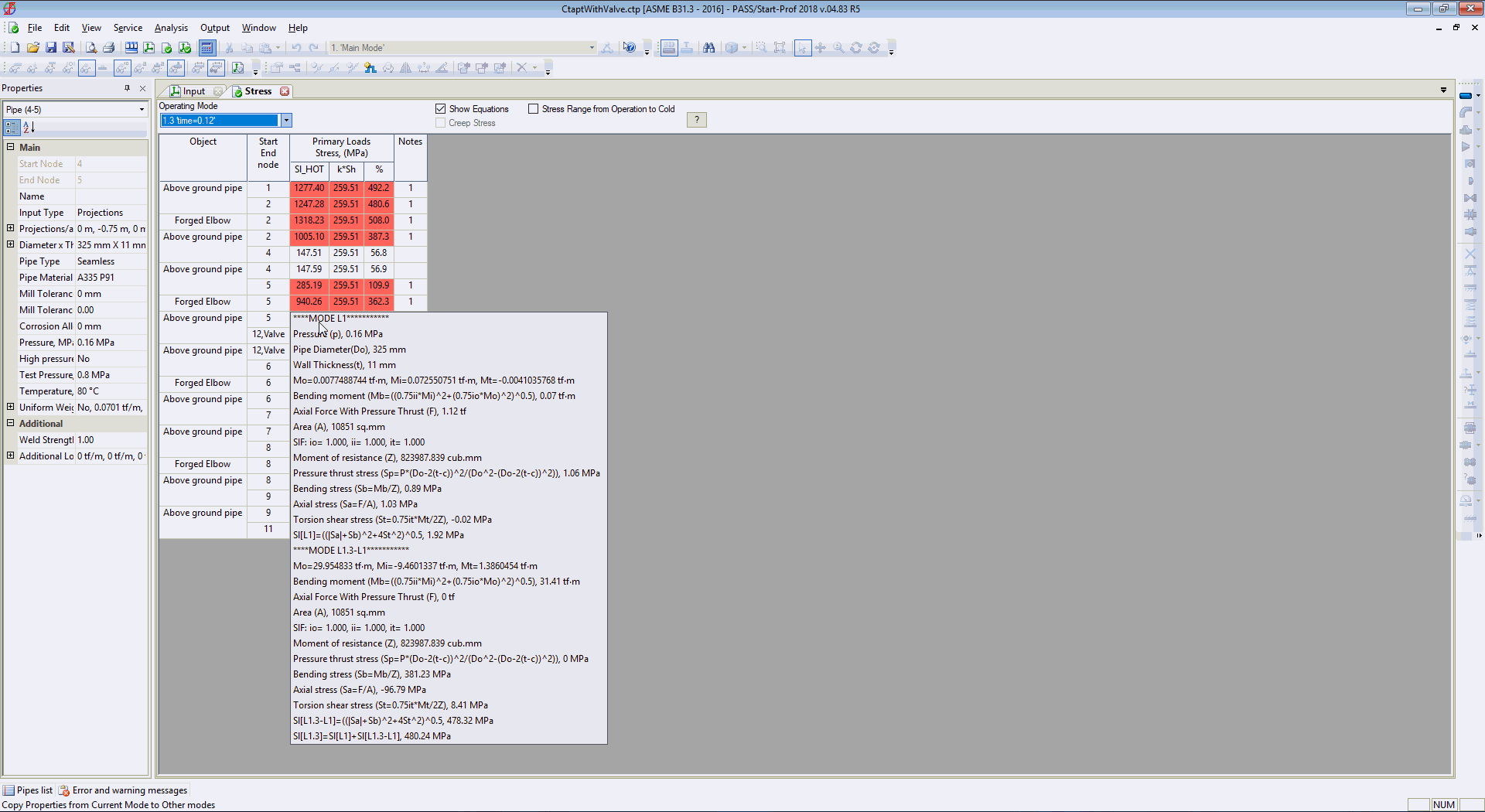
And maximum stresses from all load cases (static and all moments of time during waterhammer)
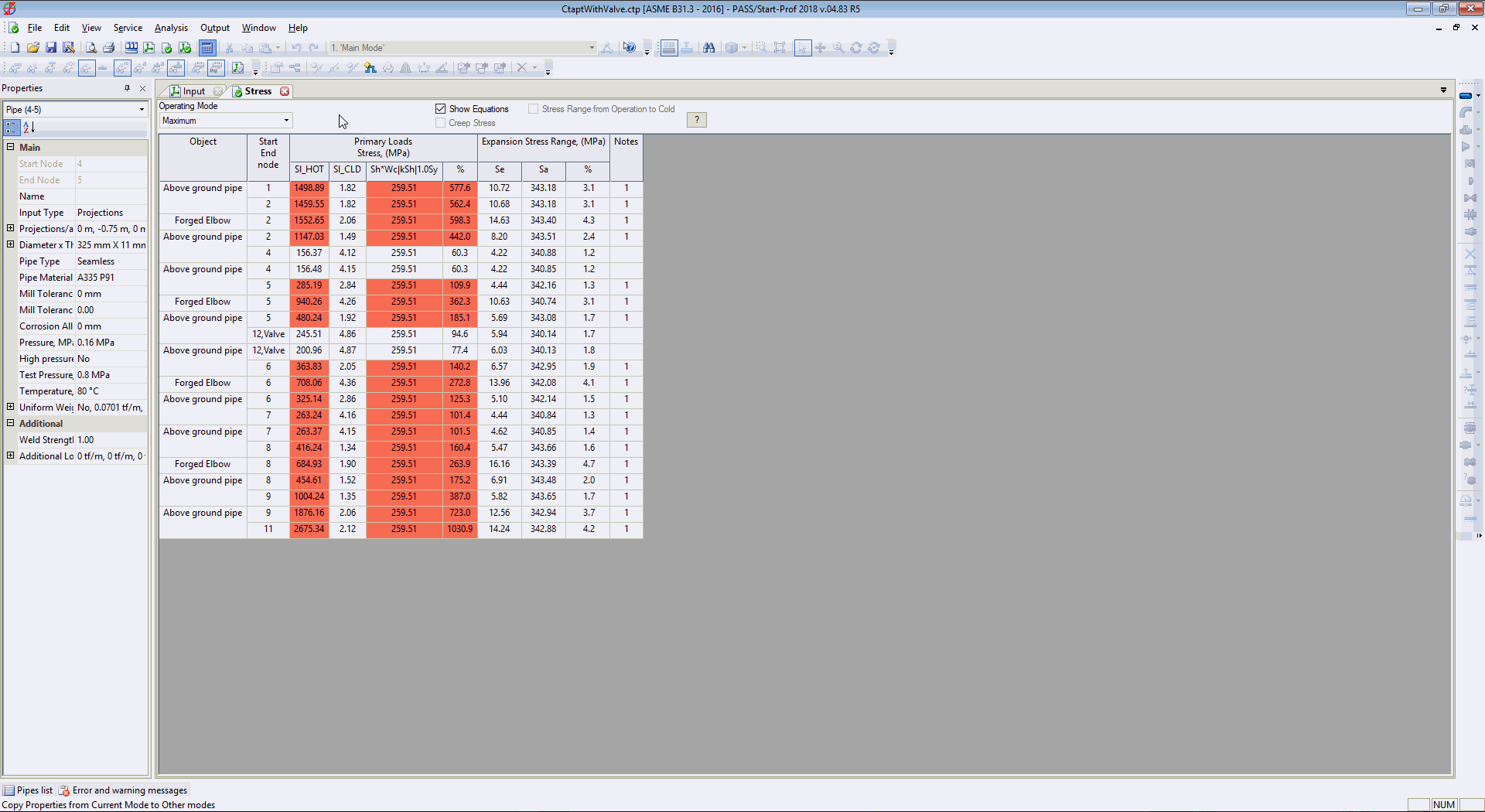
The same table can be checked for displacements, support loads, flange leakage, expansion joint deformations, etc.