


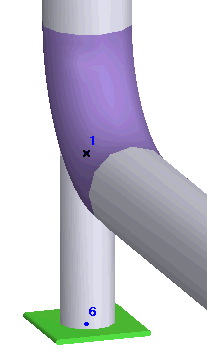
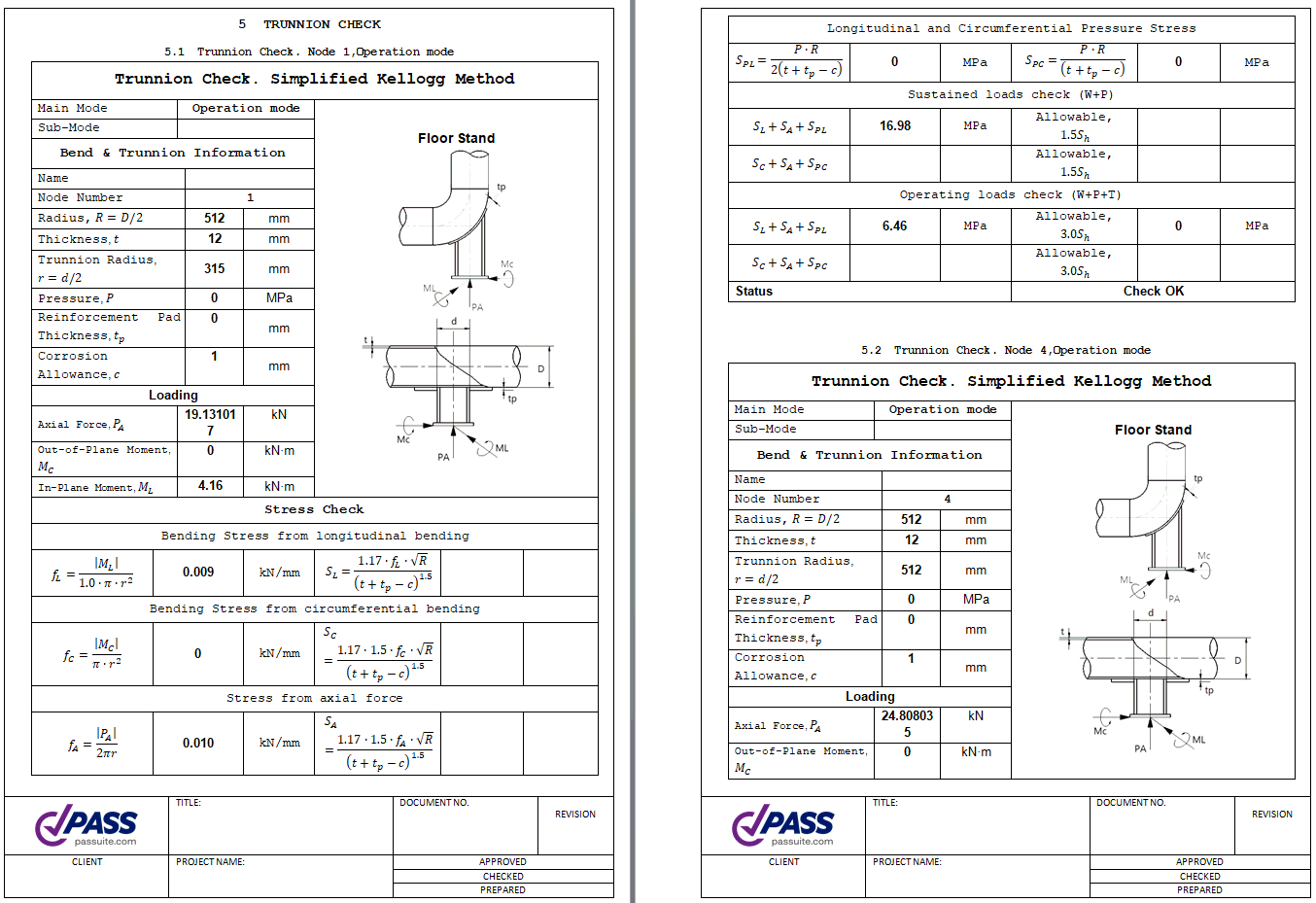
Trunnion on the bend is a pipe, connected to the bend without an opening. Trunnion element can be placed into the node of intersection of three pipe elements (like a tee element). It allows to check stress and flexibility in the junction point. After analysis the detailed report can be exported into MS Word.
Property |
Description |
Name |
Element name. If checked then it shown in 3D view |
SIF |
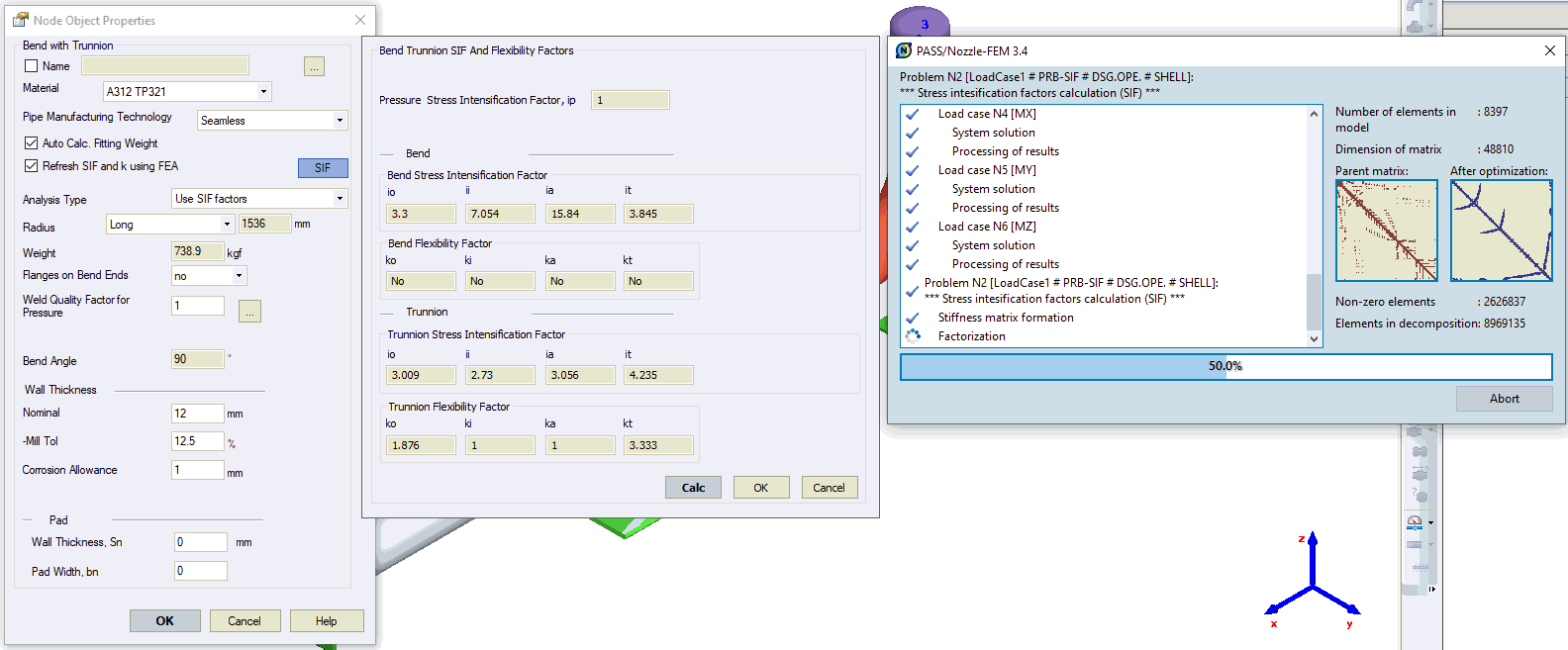
If you push this button, you will see h, SIF, k-factors for the trunnion |
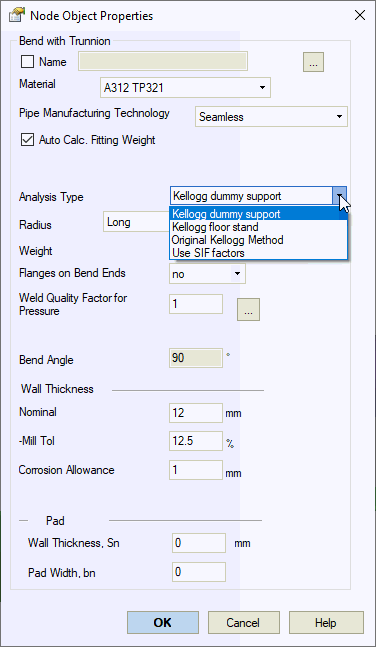
Radius, R |
Bend average radius (0.5D<R<10D). Long - 1.5DN, short - 1.0DN |
Calculate weight automatically |
If selected, reducer weight is calculated automatically as torus volume with wall thickness equal to that of adjoining pipes |
Analysis type |
There are several methods to analyze trunnions. It is simplified Kellogg method, original Kellogg method and use SIF and k factors automatically calculated using integrated finite element software PASS/NOZZLE-FEM |
Weight |
Bend weight (with flanges) without insulation and product. Set according to standards without taking into account the overload factor. Product and insulation weight with corresponding overload factors are calculated automatically based on adjoining pipes |
Longitudinal Weld Joint Efficiency Factor, E |
Longitudinal weld joint efficiency factor, E. More... |
Calculate angle automatically |
The bend angle used in bend's flexibility factor (k-factor) calculation in some codes. The option "сalculate angle automatically" should be turned on by default. It is recommended to turn off this option when the bend was splitted into several parts to model the support on bend. In this case the angle should be specified for full bend, not for each part of bend |
Angle |
|
Manufacturing technology |
For ASME B31.1, ASME B31.3, DL/T 5366-2014 seamless pipe will always use Wl=1.0. For electric-welded pipe Wl will be specified from database. More... When using GOST 32388-2013, pipe physical properties are taken from different materials databases depending on pipe type (seamless/welded). |
Material |
Material from materials database |
Presence of flanges |
Number of flanges must be selected. Flanges are rigid elements and prevent cross-section ovalization. Flanges affect the flexibility factor and stress intensification factor.
|
Nominal wall thickness, S |
Nominal (actual) wall thickness |
Mill tolerance, С1 |
Mill tolerance at the time of production. More... When analyzing based on RD 10-249-98 (section 3.3.2.8), 3 mill tolerance values must be input (С1=С11+С12): external, neutral and internal bend section, with a difference equal to the value of С12. More... |
Corrosion and wear allowance, С2 |
Corrosion and wear allowance (working mill tolerance) for wall thickness. More... |
Refresh SIF and k using FEA |
|
SIF |
When user insert the trunnion on the bend object and run analysis, the second layer advanced model is automatically created. The rigid element is inserted into the bend (node 33). Vertical pipe element inserted into the node 35. It will be "trunnion". User need to add the support into the node 36.
START-PROF automatically consider the stress intensification factors (SIF) and flexibility factors (k) in the intersection node 35.
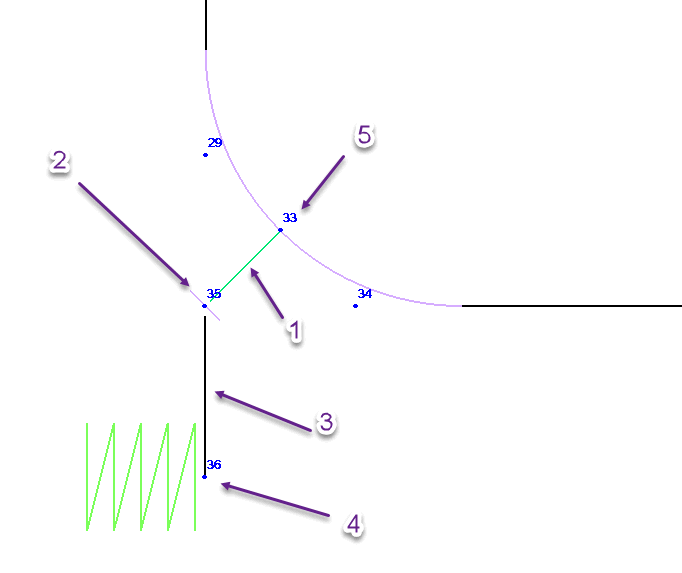
1 - rigid element, 2 - Joint element (SIF), 3 - Pipe element, 4 - Support, 5 - Node in the middle of the bend
Insert > Insert Bend > Bend with Trunnion